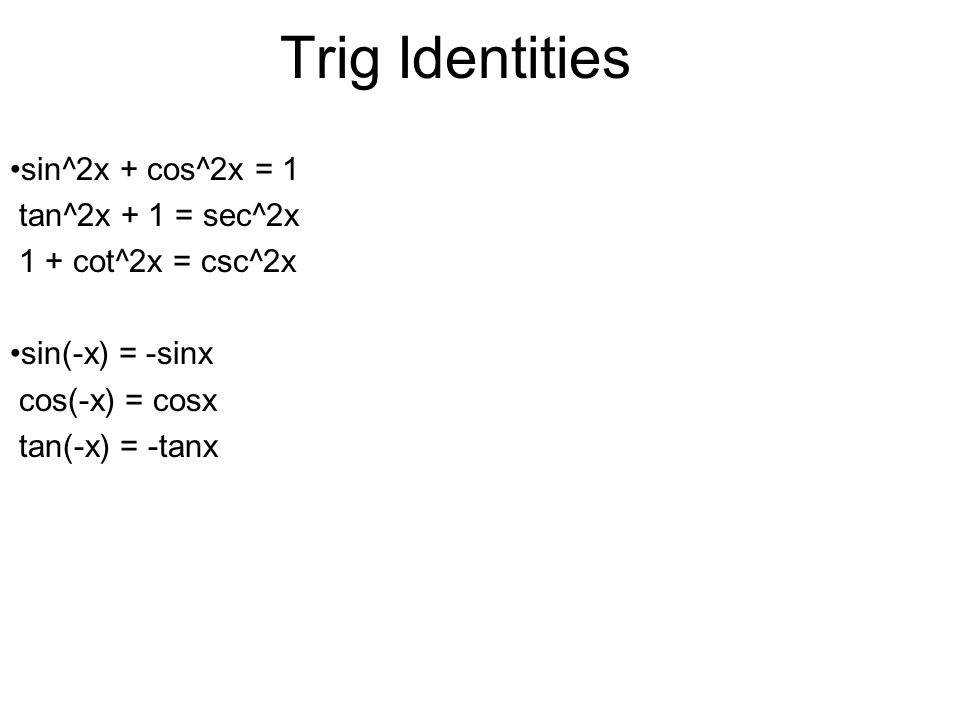
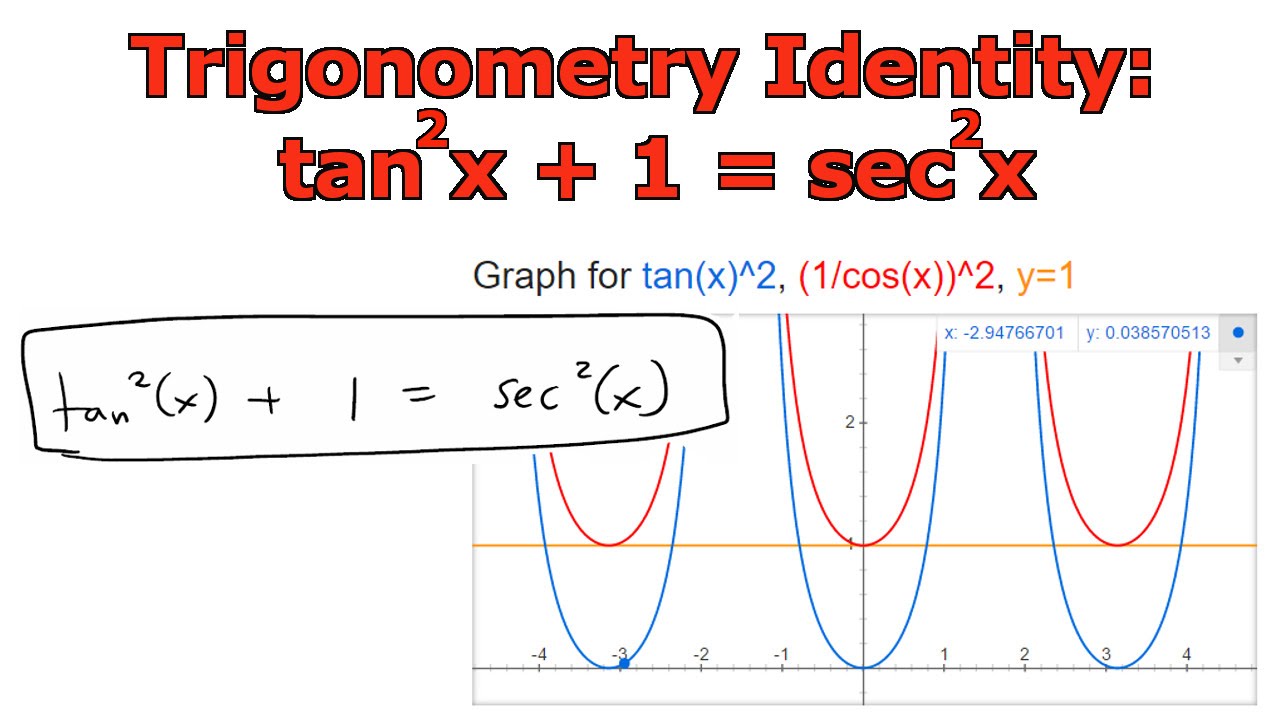
Definitions Trigonometric functions specify the relationships between side lengths and interior angles of a right triangle For example, the sine of angle θ is defined as being the length of the opposite side divided by the length of the hypotenuse The six trigonometric functions are defined for every real number, except, for some of them Trigonometry Formulas PDF – Tricks of Identities, Ratio Table, Functions Trigonometry with the help of trigonometry we can calculate angles of rightangle triangle There are 6 functions of an angle used in trigonometry and these 6 are as follow Sine (sin) Cosine (cos) Tangent (tan) Cotangent (cot) Secant (sec) Cosecant (Cosec) True Start with the well known pythagorean identity sin^2x cos^2x = 1 This is readily derived directly from the definition of the basic trigonometric functions sin and cos and Pythagoras's Theorem Divide both side by cos^2x and we get sin^2x/cos^2x cos^2x/cos^2x = 1/cos^2x tan^2x 1 = sec^2x tan^2x = sec^2x 1 Confirming that the result is an identity
上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像
Trig identities tan 2x
Trig identities tan 2x- Proving trig identity $\tan(2x)−\tan(x)=\frac{\tan(x)}{\cos(2x)}$ Ask Question Asked 4 years, 2 months ago Active 4 years, 2 months ago Viewed 4k times 1 1 $\begingroup$ I'm currently stumped on proving the trig identity below $\tan(2x)\tan (xImportant trig identities First we recall the Pythagorean identity If we begin with the cosine double angle formula, we can use the Pythagorean identity to substitute 1 cos 2 θ for sin 2 θ to obtain one of the powerreduction identities Notice that this identity allows us downconvert the power of the cosine function from 2 to 1
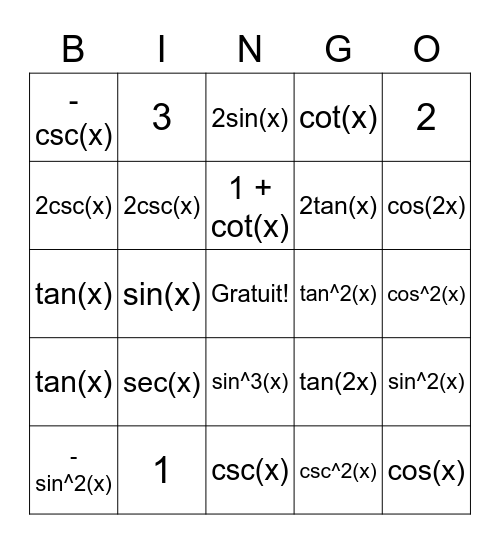



Trig Identities Bingo Card
Identities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionProve the identity Step 1) Split up the identity into the left side and right side Since the right side has a denominator that is a binomial, let's start with that side We can easily multiply it by its conjugate 1 cosx and the denominator should become 1 cos^2x (difference of squares) Step 2) Continue to simplify the right side Identities to simplify tan^4x2tan^2x1 Mathematics 1 If csc θ = 5 and θ is an acute angle, find a sin θ b cos θ 2 Use trig identities to transform the expression (sec θ)/(csc θ) into a single trig function
Trig identities or a trig substitution With A = 3x and B = 2x we have Z sin3xcos2xdx = 1 2 Z and using the identity 1tan2 θ = sec2 θ this reduces to 1 a Z 1dθ = 1 a θ c = 1 a tan−1 x a c This is a standard result which you should be aware of and be prepared to look up when necessaryTrigonometry is the branch of mathematics which is basically concerned with specific functions of angles, their applications and their calculations In mathematics, there are a total of six different types of trigonometric functions Sine (sin), Cosine (cos), Secant (sec), Cosecant (cosec), Tangent (tan) and Cotangent (cot)Pythagorean Trig Identities Pythagoras Trig Identities are the trigonometric identities which actually the true representation of the Pythagoras Theorem as trigonometric functions So, these identities help us to fundamentally decide the relationship between different sine, cosine, and tan trigonometric function
Tan(2x)= 2tan(x) 1 2tan (x) HALFANGLE IDENTITIES sin TRIGONOMETRY LAWS AND IDENTITIES DEFINITIONS sin(x)= Opposite Hypotenuse cos(x)= Adjacent Hypotenuse tan(x)= Opposite Adjacent csc(x)= Hypotenuse Opposite sec(x)= Hypotenuse Adjacent cot(x)= Adjacent Opposite Adjacent OppositeIdentities Proving Identities Trig Equations Trig Inequalities Evaluate Functions Simplify Statistics Arithmetic Mean Geometric Mean Quadratic Mean Median Mode Order Minimum Maximum Probability MidRange Range Standard Deviation Variance Lower Quartile Upper Quartile Interquartile Range Midhinge Standard Normal DistributionYou just studied 32 terms!
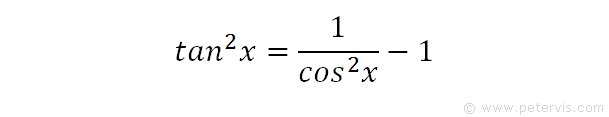



Integrate Tan 2x



Lesson 5 Multiple Angle Product To Sum Identities Trig Unit 5
trig identity for tan x = 2sin xcos x sin x sin 2 x simplify cos x = 2 sin2 x sin 2 x = 3 sin 2 x = RHS (7) There are several ways to prove this Here is one solution LHS = (tan x – 1)(sin 2x – 2cos 2 x) = (sin x – 1 ) (2sin x cos x – 2cos 2 x) double angle identity for sin 2x cos x = 2sin 2 x – 2sin x cos x – 2sin x cos xIntro to Trigonometry Identities Notes and Examples Definition of Identity An equation which is true for every value of the variable Definitions "Reciprocal Identifies" Example 4) = 3x 12 (Every value of x is true) Notes Sin CSC Sin Cos Sin x CSC x — Cos x Sec x Tan X Cot x or "Ratio Identities" (or, "Tangent Identities") oppositeQuotient Identities In trigonometry, there are a couple of quotient identities They are defined by two trigonometric functions, which are called the tangent and cotangent functions




Solved 2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove Tan Chegg Com
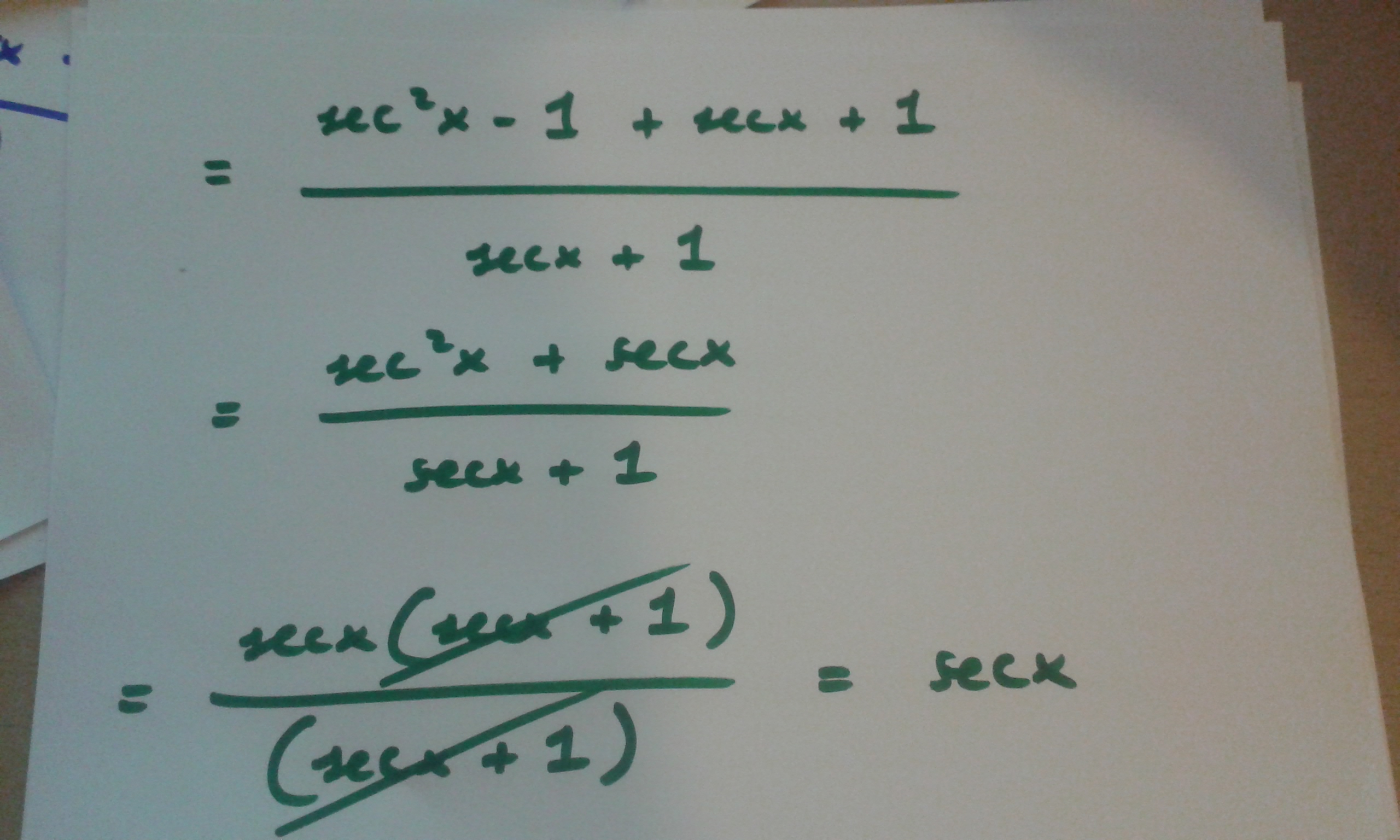



How Do You Prove Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Secx Socratic
Trigonometric Identities are useful whenever trigonometric functions are involved in an expression or an equation Trigonometric Identities are true for every value of variables occurring on both sides of an equation Geometrically, these identities involve certain trigonometric functions (such as sine, cosine, tangent) of one or more angles Sine, cosine and tangent are the primaryNow up your study game with Learn modeCos 2x is an important identity in trigonometry which can be expressed in different ways It can be expressed in terms of different trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangentCos 2x is one of the double angle trigonometric identities as the angle in consideration is a multiple of 2, that is, the double of x




Solved 2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove Tan Chegg Com
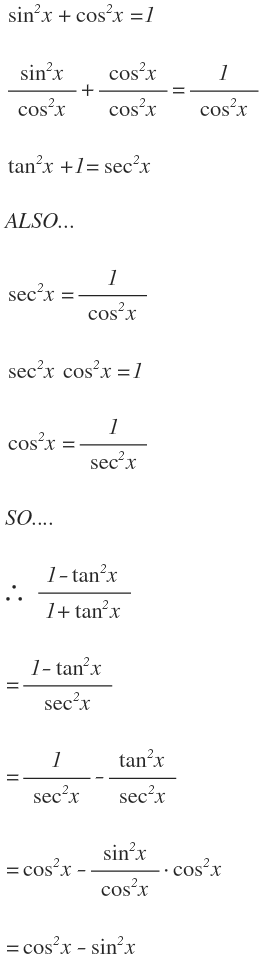



How Do You Simplify 1 Tan 2 X 1 Tan 2 X Socratic
In this video you will learn how to verify trigonometric identitiesverifying trigonometric identitieshow to verify trig identitieshow to verify trigonometricStart studying Trig Identities Learn vocabulary, terms, and more with flashcards, games, and other study toolsTrig HalfAngle Identities The halfangle identities are the identities involving functions with half angles The square root of the first two functions sine and cosine take negative or positive value depending upon the quadrant in which θ /2 lies Here is a



Analytic Trig Ppt Video Online Download



Trig Double Identities Trigonometric Double Angle Functions Trig
1 cos ( x) − cos ( x) 1 sin ( x) = tan ( x) Go!View Trigonometric Identitiespdf from PSY 7701 at East Stroudsburg Shs South Part 1 Simplify each expression a) sin^2(x) Ex (1cos x) (1 cos x) is equivalent to (1/2)(1cos (2x) using trigIn this video you will learn how to verify trigonometric identitiesverifying trigonometric identitieshow to verify trig identitieshow to verify trigonometric



Trigonometric Identities All In One Cheat Sheet Docsity



How To Solve Tan 2xsin 2x Tan 2x Sin 2x Trigonometry Trigonometric Identities Youtube
Tan 2x Formula What Is Tan 2x Formula Examples Trig identities tan^2 Trig identities tan^2Section 71 Solving Trigonometric Equations and Identities 413 Try it Now 2 Solve 2 2sin ( ) 3cos(t t ) for all solutions t 0 2 In addition to the Pythagorean identity, it In mathematics, inverse trigonometric functions are also known as arcus functions or antitrigonometric functions The inverse trigonometric functions are the inverse functions of basic trigonometric functions, ie, sine, cosine, tangent, cosecant, secant, and cotangent It is used to find the angles with any trigonometric ratioThe more important identities You don't have to know all the identities off the top of your head But these you should Defining relations for tangent, cotangent, secant, and cosecant in terms of sine and cosine The Pythagorean formula for sines and cosines This is probably the most important trig identity




Warm Up Prove Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 This Is One Of 3 Pythagorean Identities That We Will Be Using In Ch 11 The Other 2 Are 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Ppt Download




Fastest What Is Tan 2x Equal To
Proving Trigonometric Identities Calculator Get detailed solutions to your math problems with our Proving Trigonometric Identities stepbystep calculator Practice your math skills and learn step by step with our math solver Check out all of our online calculators here!USEFUL TRIGONOMETRIC IDENTITIES De nitions tanx= sinx cosx secx= 1 cosx cosecx= 1 sinx cotx= 1 tanx Fundamental trig identity (cosx)2 (sinx)2 = 1 1(tanx)2 = (secx)2 (cotx)2 1 = (cosecx)2 Odd and even properties cos( x) = cos(x) sin( x) = sin(x) tan( x) = tan(x) Double angle formulas sin(2x) = 2sinxcosx cos(2x) = (cosx)2 (sinx)2 cos(2x) = 2Tan = = = x x y x x opp adj x sin cos tan 1 cot = = = = Pythagorean IdentitiesPythagorean Identities sin 2x cos2x = 1 cos2x = 1 – sin 2x sin 2x = 1 cos2x tan 2x – sec2x = 1 1 tan 2x = sec2x 1 cot2x = csc2x Sum or difference of two angles Trig Identities Cheat Sheet



Exam Questions Trigonometric Identities Examsolutions
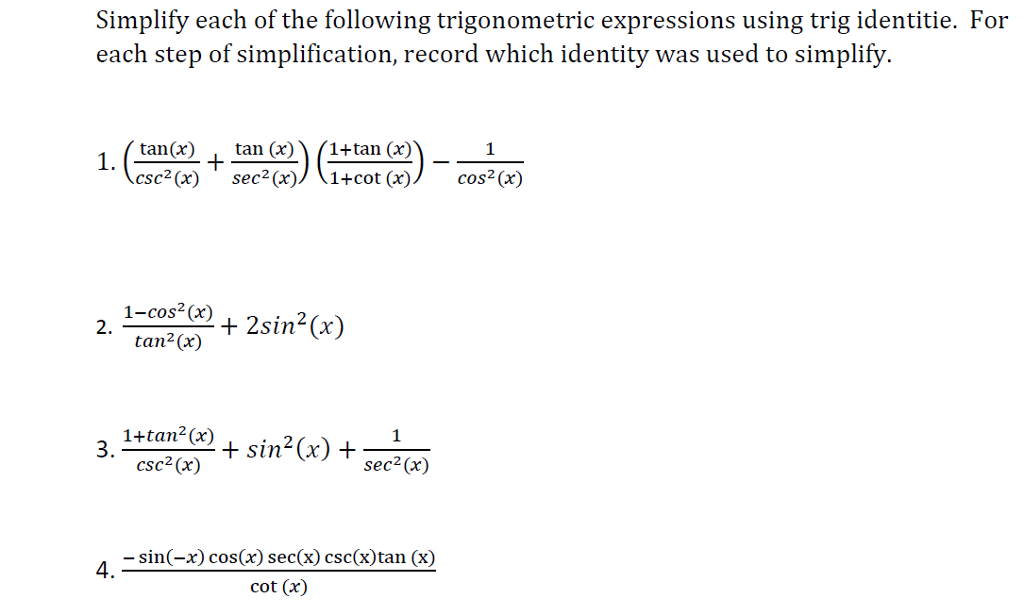



Solved Simplify Each Of The Following Trigonometric Chegg Com
Trig identities are trigonometry equations that are always true, and they're often used to solve trigonometry and geometry problems and understand various mathematical properties Knowing key trig identities helps you remember and understand important mathematical principles and solve numerous math problems The 25 Most Important Trig IdentitiesTrig Identities Nice work!Integrate tan^22x To integrate tan^22x, also written as ∫tan 2 2x dx, tan squared 2x, (tan2x)^2, and tan^2 (2x), we start by utilising standard trig identities to change the form of the integral Our goal is to have sec 2 2x in the new form because there is a standard integration solution for that in formula booklets that we can use



Solved Prove The Following Trig Identity Sec 2 X 2secx Cosx Cos 2 X Tan 2 X Sin 2 X Course Hero




What Is Tan Squared
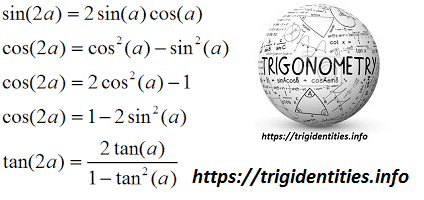
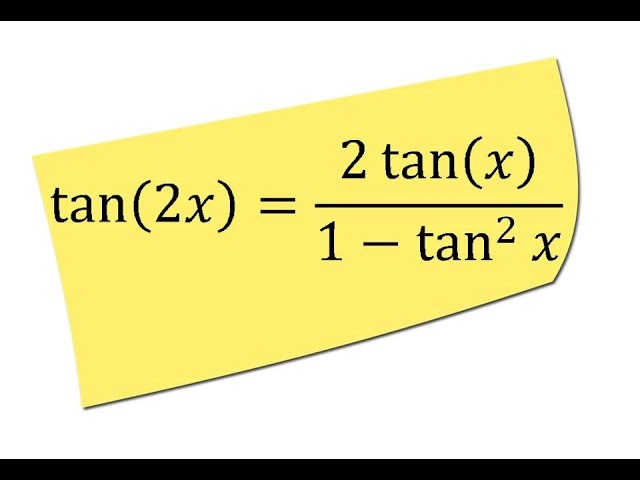
Tan(x y) = (tan x tan y) / (1 tan x tan y) sin(2x) = 2 sin x cos x cos(2x) = cos 2 (x) sin 2 (x) = 2 cos 2 (x) 1 = 1 2 sin 2 (x) tan(2x) = 2 tan(x) / (1Free math lessons and math homework help from basic math to algebra, geometry and beyond Students, teachers, parents, and everyone can find solutions to their math problems instantlyBasic Trig Identities The basic trig identities or fundamental trigonometric identities are actually those trigonometric functions which are true each time for variablesSo, these trig identities portray certain functions of at least one angle (it could be more angles) It is identified with a unit circle where the connection between the lines and angles in a Cartesian plane




Trig Identities Wksht2 Pdf Geometry Lie Groups




How Do You Prove The Identities Cosx Secx Sinx Cscx Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic
Trig Identities Identities involving trig functions are listed below Pythagorean Identities sin 2 θ cos 2 θ = 1 tan 2 θ 1 = sec 2 θ cot 2 θ 1 = csc 2 θ Reciprocal IdentitiesList of trigonometric identities 2 Trigonometric functions The primary trigonometric functions are the sine and cosine of an angle These are sometimes abbreviated sin(θ) andcos(θ), respectively, where θ is the angle, but the parentheses around the angle are often omitted, eg, sin θ andcos θ The tangent (tan) of an angle is the ratio of the sine to the cosine Tan 2x 2 tan x Tangent doubleangle identity can be accomplished by applying the same The halfangle identity for tangent can be written in three different forms I need to prove this identity tan2xsin2x tan2xsin2x start with left side Verify the identity tan α2 1 cos αsin α Trigonometric functions specify the relationships between side



A Trig Identity




Double Angle Trig Identities Quiz Quiz Quizizz
Trig Use fundamental identities and or the complementary angle theorem to find the value of the expression tan 55°cos 35°/sin 35° a) sqrt2/2 b) sqrt3 c) sqrt3/2 d) sqrt2 e) 0 f) 1 trig Given that tan B= 7/24 with B in quadrant III, find sin 2B, cos 2B, and tan 2B, using angle identities mathTrig Cheat Sheet Definition of the Trig Functions Right triangle definition For this definition we assume that 0 2 pSimplify trigonometric expressions Calculator online with solution and steps Detailed step by step solutions to your Simplify trigonometric expressions problems online with our math solver and calculator Solved exercises of Simplify trigonometric expressions



Tan2x 1 ただの悪魔の画像




How To Use Trig Identities Mathematics Stack Exchange
Trigonometric identities reciprocal identities pythagorean = x sum and sin x sin tan ± y doubleangle identities 2x = 2 = = x — x — tan x




Solved 2 Prove The Following Trig Identities A Prove Tan Chegg Com




Domaine De Definition De Tan 2x




上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像



Trigonometric Identities Learn Trigonometry By Ib Elite Tutor




Fastest Prove The Identity Tan X Sin 2x 1 Cos 2x



Verifying A Trigonometric Identity Cos X 1 Tan 2 X Cos X Sec X 1 Youtube



Tan 2x Formula What Is Tan 2x Formula Examples



What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora




List Of Trigonometric Identities Wikipedia




70pmylqshcbm



3
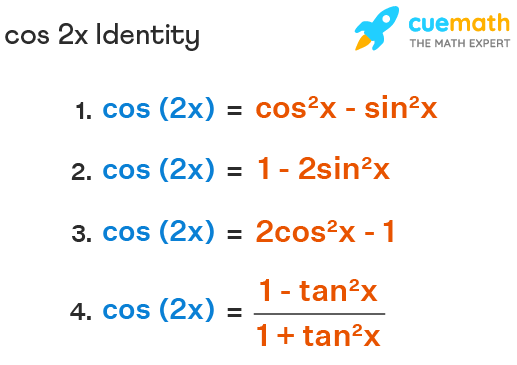



Cos 2x Formula Derivation Examples What Is Cos 2a Formula




Trig Identities Turn The Wheel



Solved Prove The Following Trig Identities Course Hero



3




Trigonometric Identities Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes




Half Angle Calculator




Solved Inquiry 11 8 Marks Prove The Following Trig Chegg Com
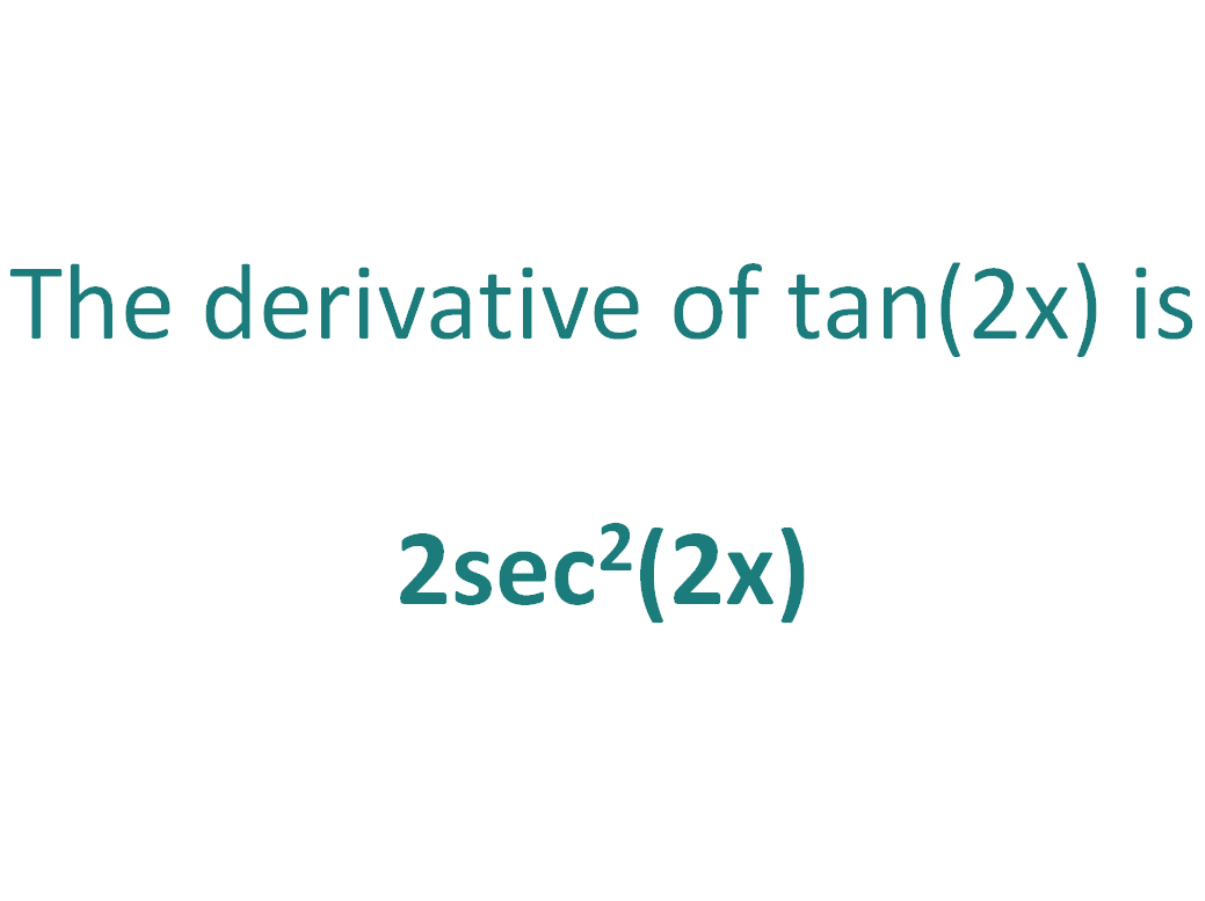



Trigonometric Functions Derivativeit



View Question For Questions 1 5 Decide Whether The Equation Is A Trigonometric Identity Explain Your Reasoning
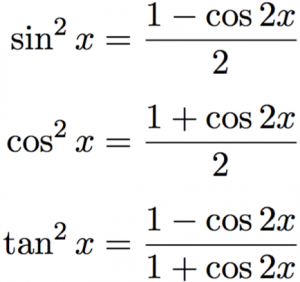



上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像




While You Wait Trigonometric Identities And Equations Section




Example 1 Verify A Trigonometric Identity The Left Hand Side Of This Identity Is More Complicated So Transform That Expression Into The One On The Right Ppt Download
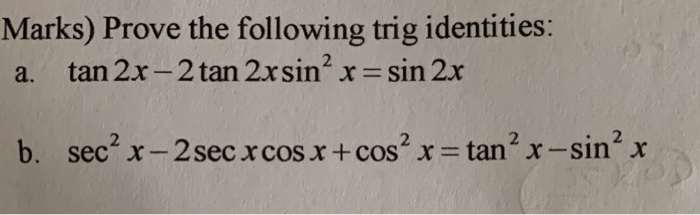



Solved 3 Marks A Swimmer On A Floating Air Mattress Will Chegg Com
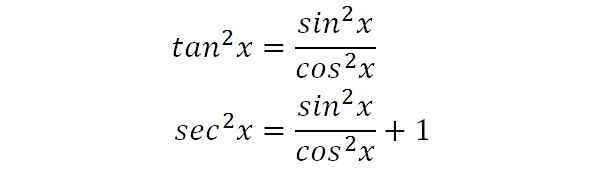



Integrate Sec 2x Method 2




Trig Identities Bingo Card




上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像



Answered O Trigonometric Identities And Bartleby




Solved Verify That The Equation Is An Identity Tan 2x Cot Chegg Com




Trigonometric Identities And Examples With Worksheets



1



Trigonometry Identity Tan 2 X 1 Sec 2 X Youtube




bestpictjcry Tan 2x Tan 2x



Tan2x 2tanx 1 Tan X Trigonometric Identity Solve Hindi Youtube
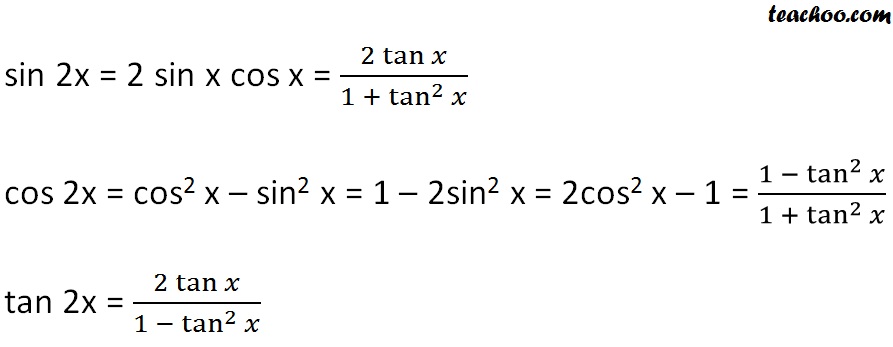



Double Angle Formulas Trigonometry Teachoo 2x 3x Formula Provi



Tan2x ただの悪魔の画像
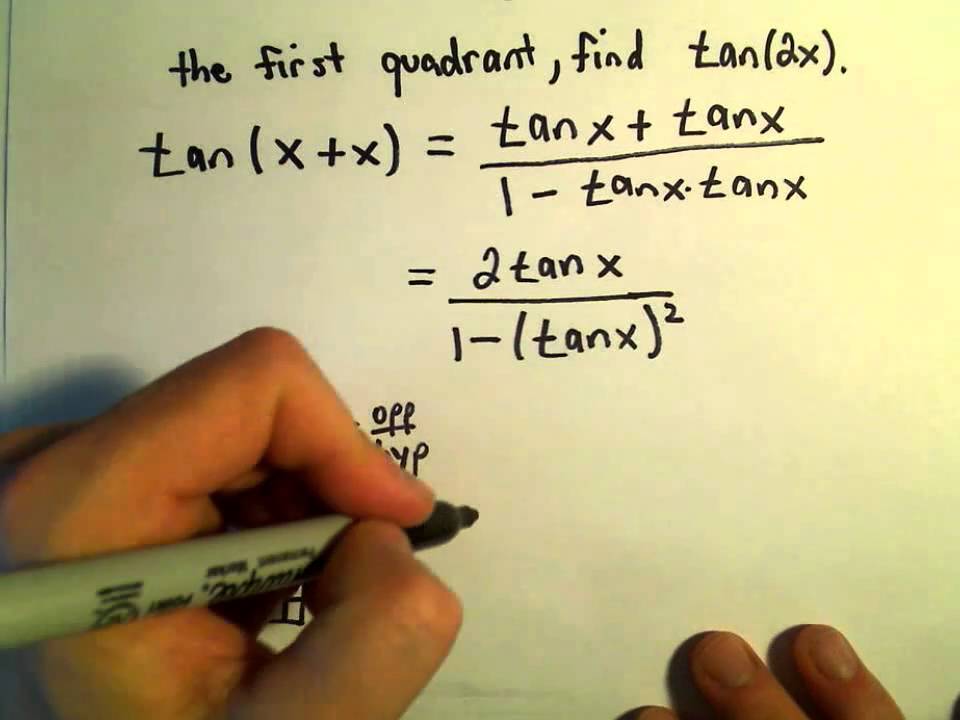



Sum And Difference Identities Video Lessons Examples And Solutions




Using Trigonometric Identities Video Khan Academy
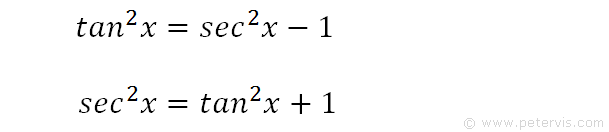



Integrate Sec 2x Method 1



Trig Identities Bingo Card




Cos 2x
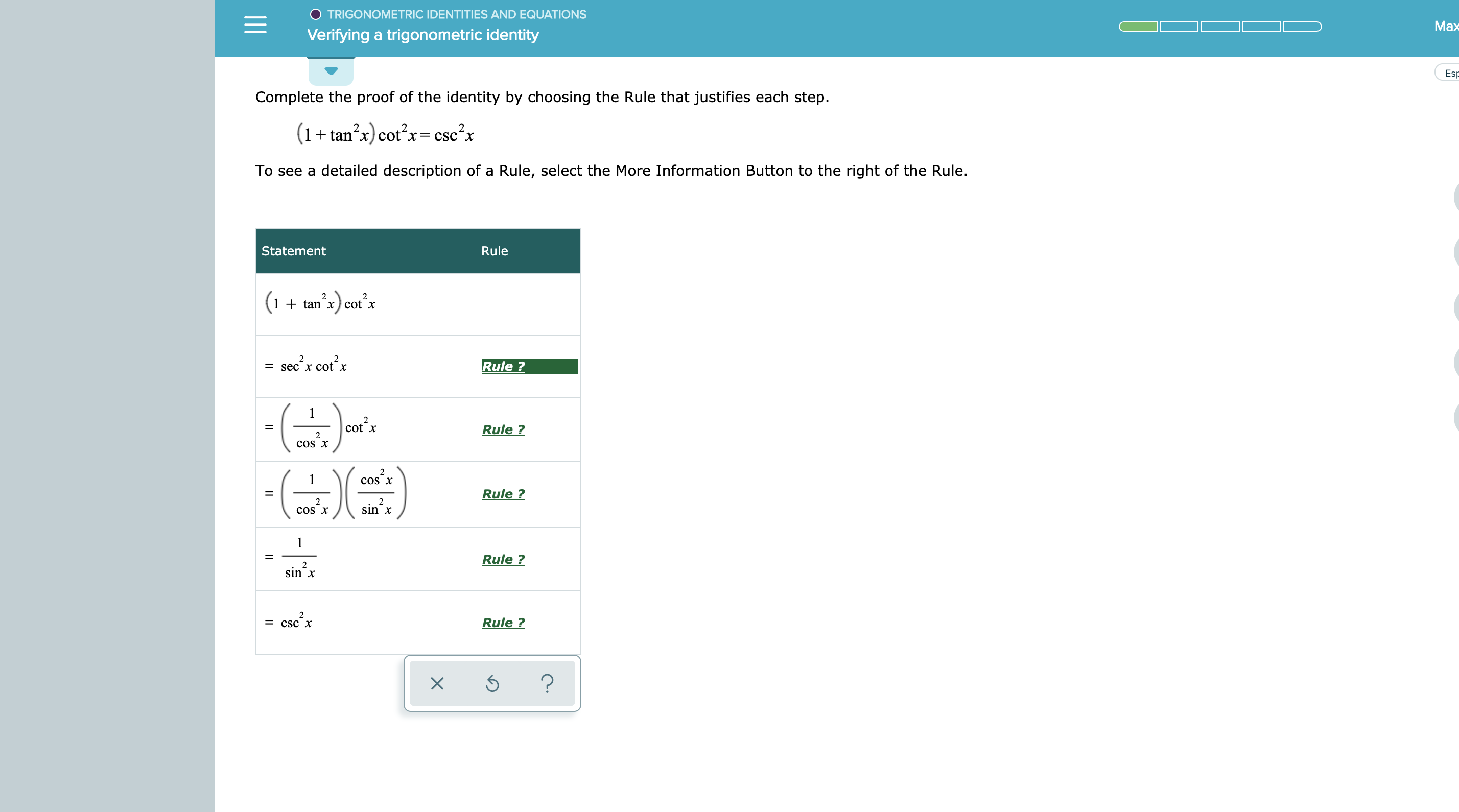



Answered Trigonometric Identities And Equations Bartleby
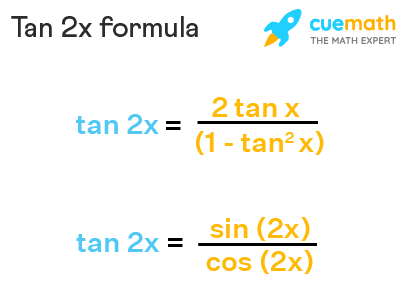



Tan 2x Formula What Is Tan 2x Formula Examples




上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像



1



Ilectureonline



View Question Trig Identities Need Help



上 Tan2x Identity ただの悪魔の画像



What Is The Integration Of Tan 2x Solution Quora



Precalc Wup 216 Using Trig Identities 2 Simplify




Alternate Forms Of Trigonometric Identities Video Lesson Transcript Study Com



Tan2x Tan 2x Identity For Tan2x Proof Of Tan2x Identity Formula For Tan2x Youtube
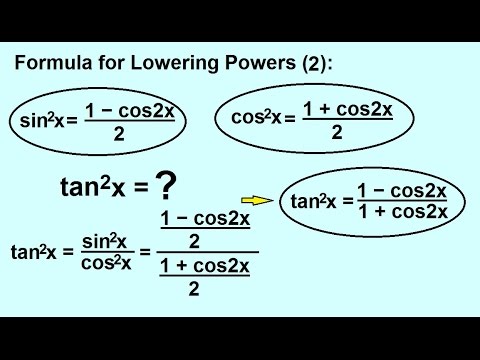



Precalculus Trigonometry Trig Identities 29 Of 57 Formula For Lowering Power Tan 2 X Youtube



What Is The Formula Of Tan2x Quora
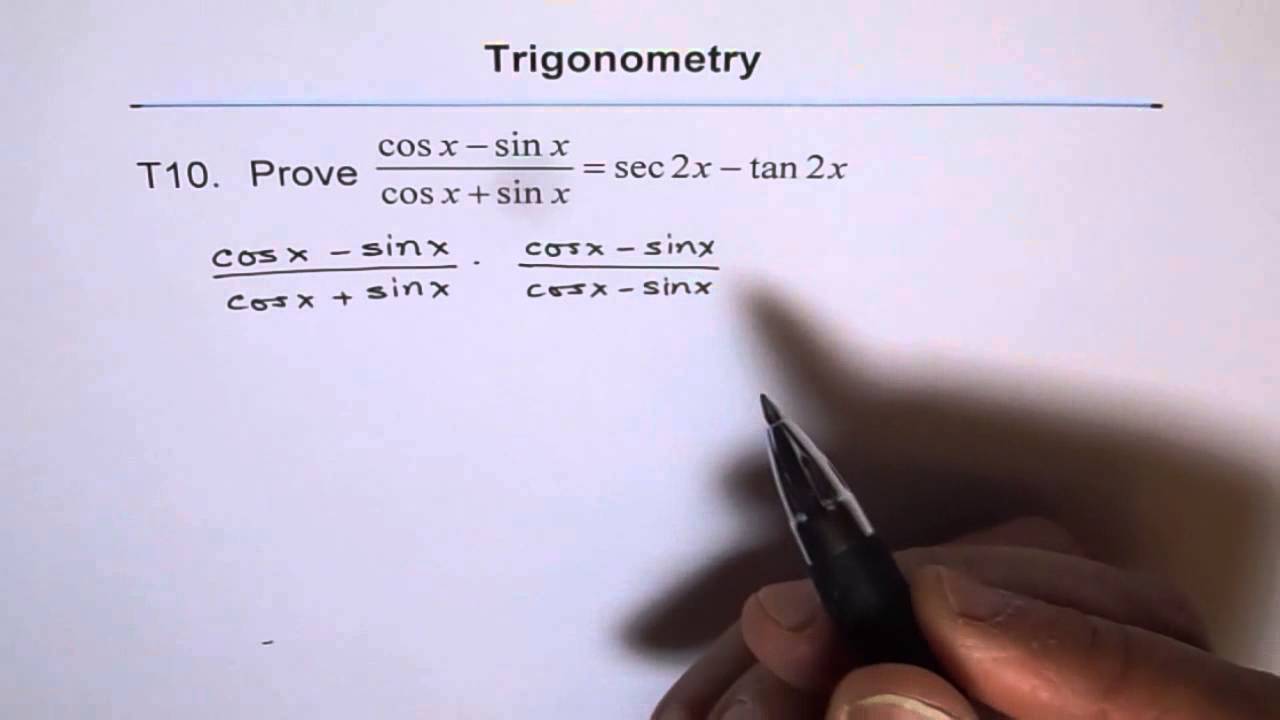



Trig Identity Sec2x Minus Tan2x T10 Youtube
x-1=sec(squared)x.jpg)



10 Identity Tan Squared X 1 Sec Squared X Trigonometry Educator Com



2




Derivatives Of Trigonometric Functions




Chapter 11 Trigonometric Identities And Equations 11 1




Warm Up Prove Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 This Is One Of 3 Pythagorean Identities That We Will Be Using In Ch 11 The Other 2 Are 1 Tan 2 X Sec 2 X Ppt Download
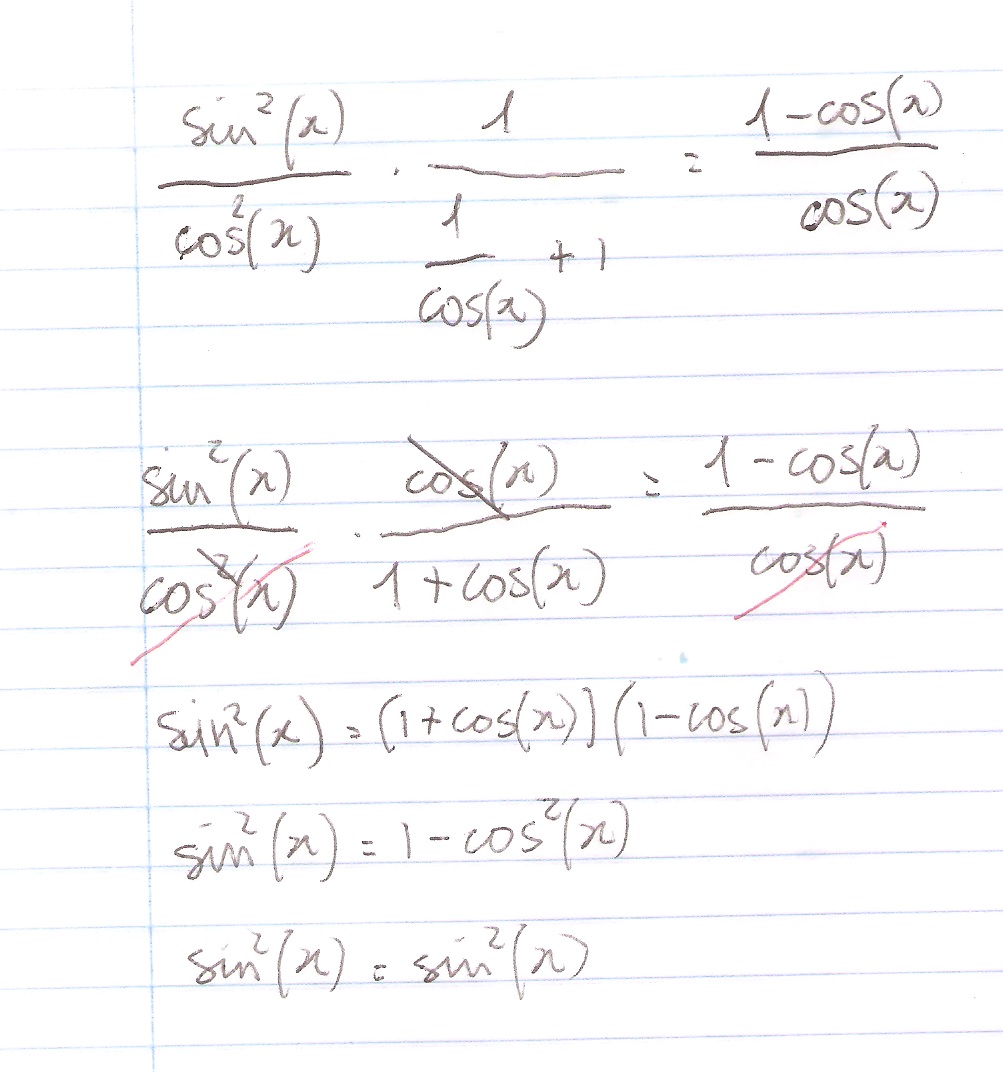



How Do You Prove The Identity Tan 2x Secx 1 1 Cosx Cosx Socratic



2
.JPG)



Every Day I M Calculatin I D3 Unit Q Pythagorean Identities
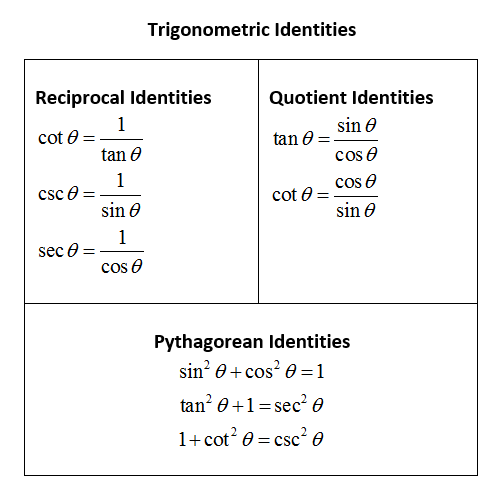



Trigonometric Identities Simplify Expressions Video Lessons Examples And Solutions
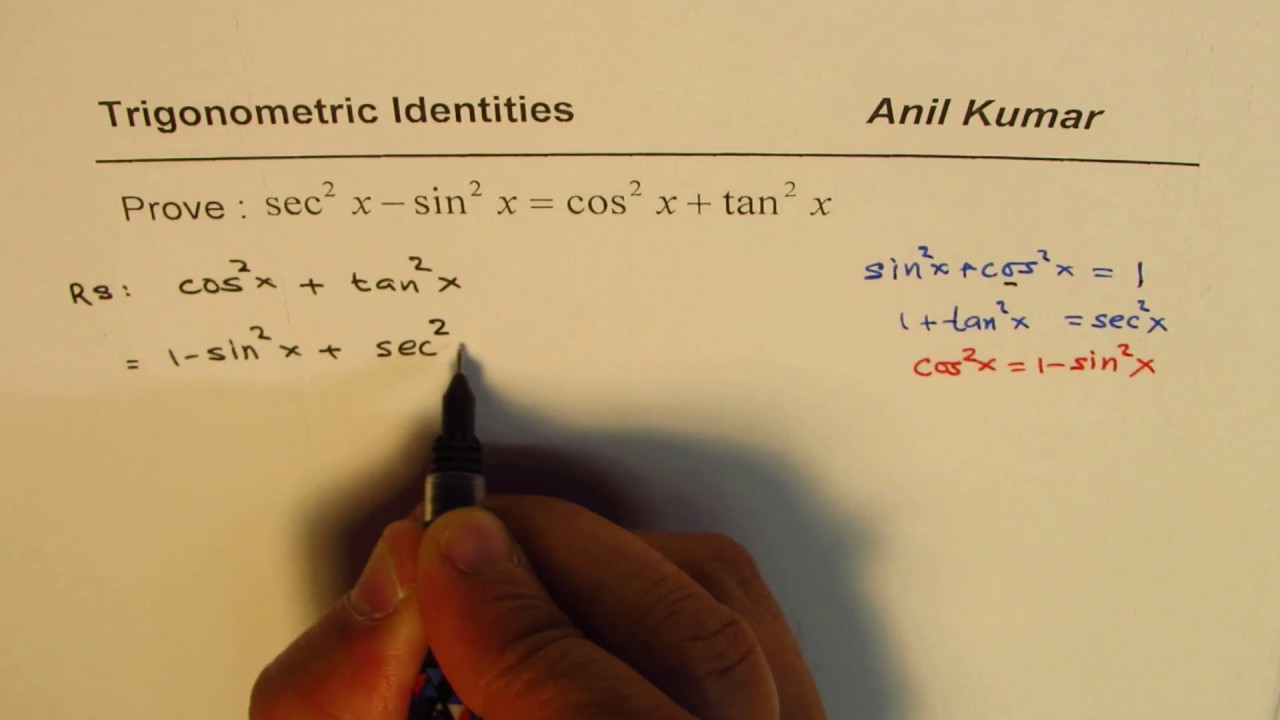



Trigonometric Identity With Pythagorens Sec 2x Sin 2x Cos 2x Tan 2x Youtube



Trig Identities Hsn Forum




Tan 2x Csc 2x Tan 2x 1 Problem Solving Solving Identity
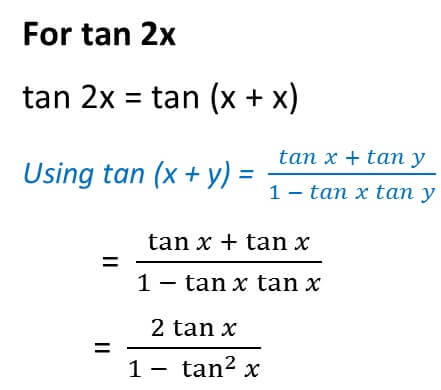



Double Angle Formulas Trigonometry Teachoo 2x 3x Formula Provi




Trig Identities Assignment Math Forums
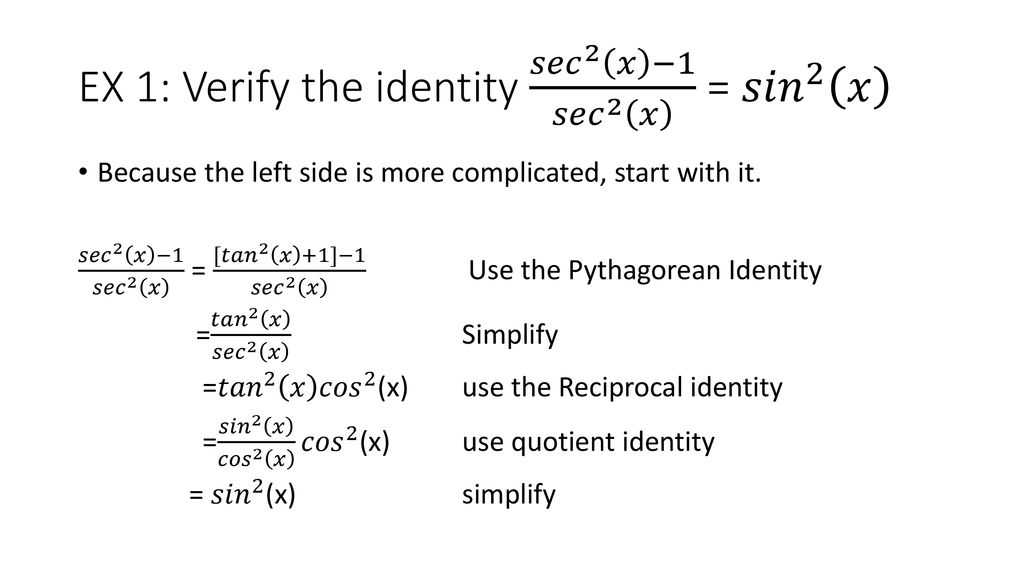



Ch Ppt Download




Trigonometric Identities Edexcel A Level Maths Pure Revision Notes



bestpictjcry Tan 2x Tan 2x
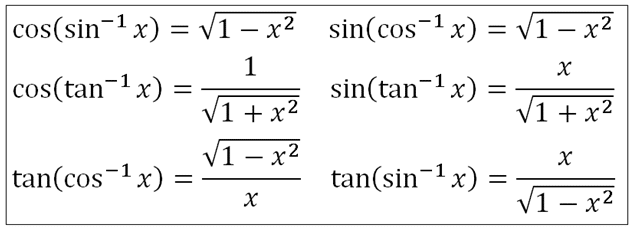



Inverse Trig Identities Reciprocal Of Trigonometric Function Trig
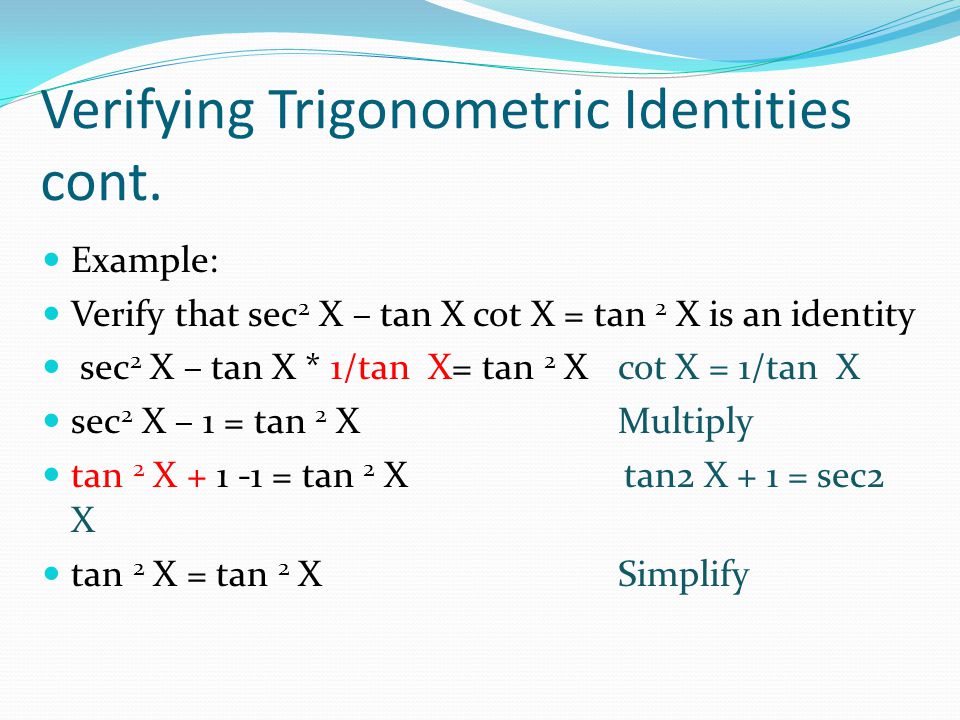



Chapter 7 Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Download
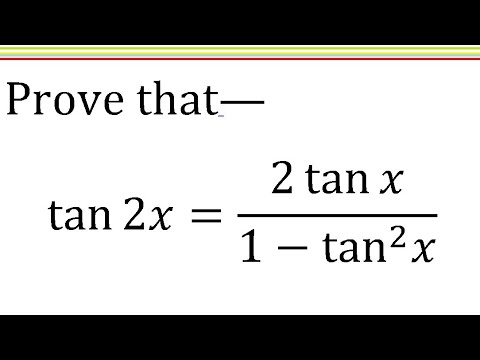



Tan2x 2tanx 1 Tan X Trigonometric Identity Solve Hindi Youtube



Cos2x Identity
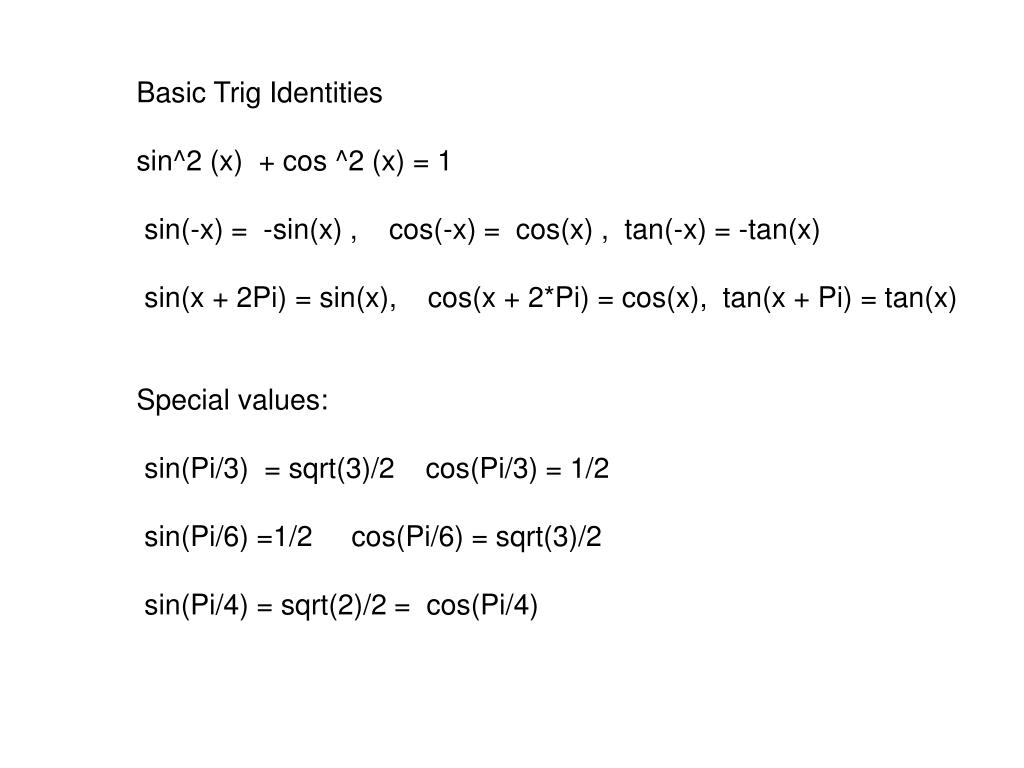



Ppt Basic Trig Identities Sin 2 X Cos 2 X 1 Powerpoint Presentation Id




How Do You Simplify Sec 4x Tan 4x Sec 2x Tan 2x Socratic




Show That The Following Are Not Trigonometric Identities 1 Tan 2x 2tan X 2 Sec X Sqrt 1 Tan 2 X 3 Sin X Y Sin X Sin Y Study Com




Ch 7 Trigonometric Identities And Equations Ppt Video Online Download




Trig Identities Calc I
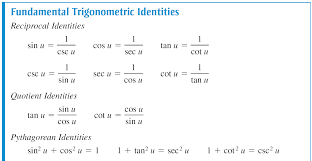



How Do You Use The Fundamental Trigonometric Identities To Determine The Simplified Form Of The Expression Socratic



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿